Code: Physical memory allocator
大雑把にやろうとしていること
- 連結リスト
freelistに物理メモリをページ単位で登録する。(kinit1(), kinit2())kalloc.c16 struct run { 17 struct run *next; 18 }; 19 20 struct { 21 struct spinlock lock; 22 int use_lock; 23 struct run *freelist; 24 } kmem;
- メモリをほしい人に割り当てができるようにする。(kalloc())
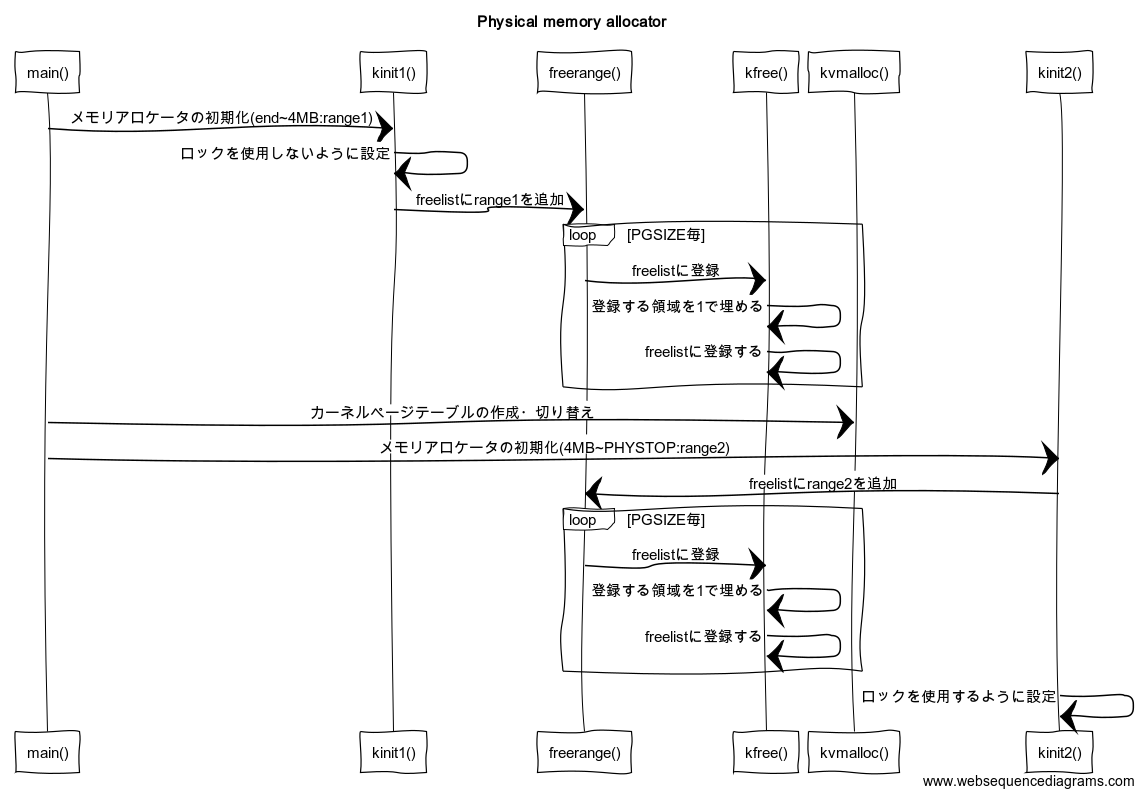
シーケンス図
ざっくりとした流れです。 関数の中身をみていていま自分がどこにいるのかわからなくなったら適宜見るとよいかもしれません。
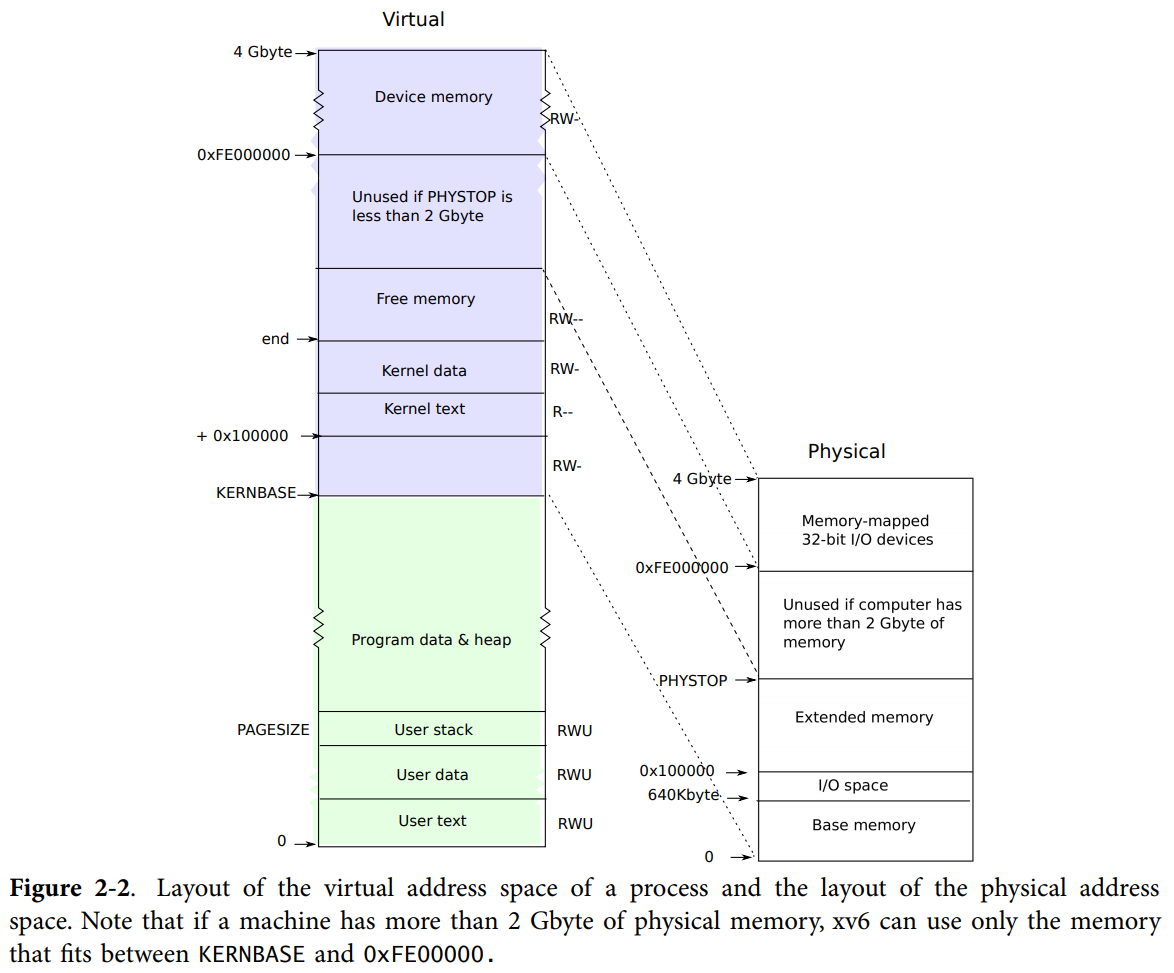
メモリレイアウト(再掲載)
前の記事で説明したメモリレイアウトの図です。 本章でもかなり使うので載せておきます。適宜確認してください。
Source: commentary/textbook
VAとPAの関係表です。
| 名前 | 仮想アドレス | 物理アドレス |
|---|---|---|
| end | end | V2P(end) |
| PHYSTOP | P2V(PHYSTOP) | PHYSTOP |
| KERNBASE | KERNBASE | V2P(KERNBASE) |
main()
main.c17 int 18 main(void) 19 { 20 kinit1(end, P2V(4*1024*1024)); // phys page allocator 21 kvmalloc(); // kernel page table ~~~ 35 kinit2(P2V(4*1024*1024), P2V(PHYSTOP)); // must come after startothers() ~~~ 38 }- L20: end~4MBまでをページアロケータに登録
- L20までのPDTは
entrypgdirmain.c97 // The boot page table used in entry.S and entryother.S. 98 // Page directories (and page tables) must start on page boundaries, 99 // hence the __aligned__ attribute. 100 // PTE_PS in a page directory entry enables 4Mbyte pages. 101 102 __attribute__((__aligned__(PGSIZE))) 103 pde_t entrypgdir[NPDENTRIES] = { 104 // Map VA's [0, 4MB) to PA's [0, 4MB) 105 [0] = (0) | PTE_P | PTE_W | PTE_PS, 106 // Map VA's [KERNBASE, KERNBASE+4MB) to PA's [0, 4MB) 107 [KERNBASE>>PDXSHIFT] = (0) | PTE_P | PTE_W | PTE_PS, 108 };- L105: VA: [0 ~ 4MB)→ PA: [0 ~ 4MB)
- L106: VA: [KERNBASE ~ KERNBASE+4MB)→ PA[0 ~ 4MB)
両方とも同じPAにマッピングしている
- L21: カーネルのPDTを作成、設定
- L22: 4MB~PHYSTOPまでをページアロケータに登録
- kinit1()とkinit2()の2回にわけてページアロケータに登録している理由
kinit1()
kallo.c26 // Initialization happens in two phases. 27 // 1. main() calls kinit1() while still using entrypgdir to place just 28 // the pages mapped by entrypgdir on free list. 29 // 2. main() calls kinit2() with the rest of the physical pages 30 // after installing a full page table that maps them on all cores. 31 void 32 kinit1(void *vstart, void *vend) 33 { 34 initlock(&kmem.lock, "kmem"); 35 kmem.use_lock = 0; 36 freerange(vstart, vend); 37 }vstart: end,vend: P2V(410241024)- L34 - 35: ロックを初期化してオフにする(詳細はLocking)
ロックを使用するにはメモリアロケータが必要になるのでまだ使えない - L36:
freelistに領域(vstart~vend)を登録する
freerange()
kalloc.c46 void 47 freerange(void *vstart, void *vend) 48 { 49 char *p; 50 p = (char*)PGROUNDUP((uint)vstart); 51 for(; p + PGSIZE <= (char*)vend; p += PGSIZE) 52 kfree(p); 53 }- L50:
PGSIZEに合わせてアライン - L51 - 52: ページサイズごとにkfree()を呼び出す
- L50:
kfree()
引数のアドレス(ページの先頭アドレス)をfreelistから消去
kalloc.c54 //PAGEBREAK: 21 55 // Free the page of physical memory pointed at by v, 56 // which normally should have been returned by a 57 // call to kalloc(). (The exception is when 58 // initializing the allocator; see kinit above.) 59 void 60 kfree(char *v) 61 { 62 struct run *r; 63 64 if((uint)v % PGSIZE || v < end || V2P(v) >= PHYSTOP) 65 panic("kfree"); 66 67 // Fill with junk to catch dangling refs. 68 memset(v, 1, PGSIZE); 69 70 if(kmem.use_lock) 71 acquire(&kmem.lock); 72 r = (struct run*)v; 73 r->next = kmem.freelist; 74 kmem.freelist = r; 75 if(kmem.use_lock) 76 release(&kmem.lock); 77 }- L64: エラーチェック
開始のアドレス(v)がPGSIZEの倍数であるかvがFree memory(end ~ P2V(PHYSTOP)の範囲)であるか - L68: v+PAGESIZEまで1で埋める
- L72 ~ 74: vを
freelistに登録 - L70 ~ 71, L75 ~ 76: 詳しくはLockingで
freelistを変更中にほかのスレッドに変更されるとリストが壊れるため
- L64: エラーチェック
kinit2()
kalloc.c39 void 40 kinit2(void *vstart, void *vend) 41 { 42 freerange(vstart, vend); 43 kmem.use_lock = 1; 44 }- L42: 4MB~PHYSTOPまでの物理アドレス空間をフリーリストに登録
- L44: 詳しくはLockingで
ロックを有効化
kalloc()
物理メモリ(PGSIZE分)提供
kalloc.c79 // Allocate one 4096-byte page of physical memory. 80 // Returns a pointer that the kernel can use. 81 // Returns 0 if the memory cannot be allocated. 82 char* 83 kalloc(void) 84 { 85 struct run *r; 86 87 if(kmem.use_lock) 88 acquire(&kmem.lock); 89 r = kmem.freelist; 90 if(r) 91 kmem.freelist = r->next; 92 if(kmem.use_lock) 93 release(&kmem.lock); 94 return (char*)r; 95 }- L89 - 91:
freelistから1つ取り出す - L87 - 88, L92- 93: 詳しくはLockingで
- L89 - 91:
Code: sbrk
sys_sbrk()
実行中のプロセスのメモリのサイズを増やしたり減らしたりするシステムコール
sysproc.c45 int 46 sys_sbrk(void) 47 { 48 int addr; 49 int n; 50 51 if(argint(0, &n) < 0) 52 return -1; 53 addr = myproc()->sz; 54 if(growproc(n) < 0) 55 return -1; 56 return addr; 57 }- L51 - 52: 引数の処理(詳細は後の章)
- L54: メモリを増やす(growproc())
growproc()
実行中のプロセスに割り当てるメモリを増やす。 つまり、ページングの設定を追加する
proc.c156 // Grow current process's memory by n bytes. 157 // Return 0 on success, -1 on failure. 158 int 159 growproc(int n) 160 { 161 uint sz; 162 struct proc *curproc = myproc(); 163 164 sz = curproc->sz; 165 if(n > 0){ 166 if((sz = allocuvm(curproc->pgdir, sz, sz + n)) == 0) 167 return -1; 168 } else if(n < 0){ 169 if((sz = deallocuvm(curproc->pgdir, sz, sz + n)) == 0) 170 return -1; 171 } 172 curproc->sz = sz; 173 switchuvm(curproc); 174 return 0; 175 }- L162: 実行中のプロセスの取得
- L165 - 167: 割り当てているメモリを増やす場合(allocuvm())
- L168 - 171: 割り当てているメモリを減らす場合(deallocuvm())
deallocuvm()
割り当てている物理メモリをfreelistから消去
vm.c251 // Deallocate user pages to bring the process size from oldsz to 252 // newsz. oldsz and newsz need not be page-aligned, nor does newsz 253 // need to be less than oldsz. oldsz can be larger than the actual 254 // process size. Returns the new process size. 255 int 256 deallocuvm(pde_t *pgdir, uint oldsz, uint newsz) 257 { 258 pte_t *pte; 259 uint a, pa; 260 261 if(newsz >= oldsz) 262 return oldsz; 263 264 a = PGROUNDUP(newsz); 265 for(; a < oldsz; a += PGSIZE){ 266 pte = walkpgdir(pgdir, (char*)a, 0); 267 if(!pte) 268 a = PGADDR(PDX(a) + 1, 0, 0) - PGSIZE; 269 else if((*pte & PTE_P) != 0){ 270 pa = PTE_ADDR(*pte); 271 if(pa == 0) 272 panic("kfree"); 273 char *v = P2V(pa); 274 kfree(v); 275 *pte = 0; 276 } 277 } 278 return newsz; 279 }L264:
PGSIZEにそろえるL266: 該当のPTEの捜索
- ユーザの仮想アドレスは0からスタートしているので
oldszやnewszはそのまま仮想アドレスを示す - もし、なかった場合にwalkpgidr()が割り当てることはしない(3個目の引数が0であるため)
- ユーザの仮想アドレスは0からスタートしているので
L267 - 268: 該当のPTEが存在していなかった場合
PDX(a) + 1: 仮想アドレスaが対応付けられているPDE(PDE_a)のインデックス + 1PGADDR(PDX(a) + 1, 0, 0) - PGSIZE:PDE_aの次のPDEが対応付けている先頭の仮想アドレス -PGSIZEPGSIZEが引かれているのは次のfor分でa += PGSIZEされるため
L269 - 275: 該当するPTEが存在していた
PTE_P: ページが物理メモリに存在しているかどうか(物理メモリが割り当てられているかどうか)L270: ページの先頭物理アドレス
mmu.h99 // Address in page table or page directory entry 100 #define PTE_ADDR(pte) ((uint)(pte) & ~0xFFF) 101 #define PTE_FLAGS(pte) ((uint)(pte) & 0xFFF)
L271 - 272, L275: 初期化されたPTEは0なので0だった場合はエラー
L273: 物理メモリの管理(
freelist)はカーネル領域で管理しているのでP2V()が使えるL274: 物理メモリの使用を解放
allocuvm()
新しく物理メモリを割り当てる
vm.c219 // Allocate page tables and physical memory to grow process from oldsz to 220 // newsz, which need not be page aligned. Returns new size or 0 on error. 221 int 222 allocuvm(pde_t *pgdir, uint oldsz, uint newsz) 223 { 224 char *mem; 225 uint a; 226 227 if(newsz >= KERNBASE) 228 return 0; 229 if(newsz < oldsz) 230 return oldsz; 231 232 a = PGROUNDUP(oldsz); 233 for(; a < newsz; a += PGSIZE){ 234 mem = kalloc(); 235 if(mem == 0){ 236 cprintf("allocuvm out of memory\n"); 237 deallocuvm(pgdir, newsz, oldsz); 238 return 0; 239 } 240 memset(mem, 0, PGSIZE); 241 if(mappages(pgdir, (char*)a, PGSIZE, V2P(mem), PTE_W|PTE_U) < 0){ 242 cprintf("allocuvm out of memory (2)\n"); 243 deallocuvm(pgdir, newsz, oldsz); 244 kfree(mem); 245 return 0; 246 } 247 } 248 return newsz; 249 }- L227 - 230: エラーチェック
- L232: PGSIZEにアライメント
- L233 - 247: PGSIZE毎に必要なだけ割り当てる
- L234: 割り当てる物理メモリの先頭アドレス取得(PGSIZE分)
- L234 - 239: もう割り当てるメモリがなかった場合
- L240: 0で初期化
- L241 - 246: 仮想アドレスと取得した物理メモリをマッピング
Code: exec
ユーザのカーネル空間を作るシステムコール
exec.c10 int 11 exec(char *path, char **argv) 12 { 13 char *s, *last; 14 int i, off; 15 uint argc, sz, sp, ustack[3+MAXARG+1]; 16 struct elfhdr elf; 17 struct inode *ip; 18 struct proghdr ph; 19 pde_t *pgdir, *oldpgdir; 20 struct proc *curproc = myproc(); ~~~ pathをもとに該当するinodeを取得 30 pgdir = 0; 31 32 // Check ELF header ~~~ ELFがエラーかチェック 38 if((pgdir = setupkvm()) == 0) 39 goto bad; 40 41 // Load program into memory. 42 sz = 0; 43 for(i=0, off=elf.phoff; i<elf.phnum; i++, off+=sizeof(ph)){ 44 if(readi(ip, (char*)&ph, off, sizeof(ph)) != sizeof(ph)) 45 goto bad; ~~~ エラーチェック 52 if((sz = allocuvm(pgdir, sz, ph.vaddr + ph.memsz)) == 0) 53 goto bad; 54 if(ph.vaddr % PGSIZE != 0) 55 goto bad; 56 if(loaduvm(pgdir, (char*)ph.vaddr, ip, ph.off, ph.filesz) < 0) 57 goto bad; 58 } ~~~ 63 // Allocate two pages at the next page boundary. 64 // Make the first inaccessible. Use the second as the user stack. 65 sz = PGROUNDUP(sz); 66 if((sz = allocuvm(pgdir, sz, sz + 2*PGSIZE)) == 0) 67 goto bad; 68 clearpteu(pgdir, (char*)(sz - 2*PGSIZE)); 69 sp = sz; 70 71 // Push argument strings, prepare rest of stack in ustack. ~~~ 引数などのスタックを設定 90 // Save program name for debugging. ~~~ デバッグ用の諸々 95 96 // Commit to the user image. 97 oldpgdir = curproc->pgdir; 98 curproc->pgdir = pgdir; ~~~ 諸々curprocの設定 102 switchuvm(curproc); 103 freevm(oldpgdir); 104 return 0; 105 106 bad: ~~~ エラー時の処理- L38: カーネル空間のメモリをマッピング
- L43 - 58: ELFのセグメント毎にメモリにロード
- L52: 物理メモリの割り当てる
sz: oldsizeph.vaddr + ph.memsz: newsize - L56:
ip(inode)をELFを元に所定の仮想アドレスに展開(loaduvm()) - L65 - 67: サイズがでかすぎる引数(ページを跨ぐサイズ)をきちんとエラーとして扱うために2ページ分を割り当てる
- L68: ユーザモードではアクセスできなくする
vm.c300 // Clear PTE_U on a page. Used to create an inaccessible 301 // page beneath the user stack. 302 void 303 clearpteu(pde_t *pgdir, char *uva) 304 { 305 pte_t *pte; 306 307 pte = walkpgdir(pgdir, uva, 0); 308 if(pte == 0) 309 panic("clearpteu"); 310 *pte &= ~PTE_U; 311 }
- L97, 103: 元々割り当てていた物理メモリを解放
- L98: 新しく設定したページングを割り当てる
- L102: 新しく設定したページテーブルに切り替える
loaduvm()
メモリ上にinodeのデータを展開
vm.c195 // Load a program segment into pgdir. addr must be page-aligned 196 // and the pages from addr to addr+sz must already be mapped. 197 int 198 loaduvm(pde_t *pgdir, char *addr, struct inode *ip, uint offset, uint sz) 199 { 200 uint i, pa, n; 201 pte_t *pte; 202 203 if((uint) addr % PGSIZE != 0) 204 panic("loaduvm: addr must be page aligned"); 205 for(i = 0; i < sz; i += PGSIZE){ 206 if((pte = walkpgdir(pgdir, addr+i, 0)) == 0) 207 panic("loaduvm: address should exist"); 208 pa = PTE_ADDR(*pte); 209 if(sz - i < PGSIZE) 210 n = sz - i; 211 else 212 n = PGSIZE; 213 if(readi(ip, P2V(pa), offset+i, n) != n) 214 return -1; 215 } 216 return 0; 217 }- L203: アライメントされているかチェック
- L205 - 215: PGSIZE毎に物理メモリにinodeのデータを展開
- L206 - 208: 該当する物理アドレスを仮想アドレスから探す
- L209 - 212: 読み込むサイズがPGSIZEよりも大きければPGSIZE分読み込む
- L213 - 214: データを展開(詳細はファイルシステムの章)
ip: inodeP2V(pa): 読み込む先(dst)offset+i:dstから何バイト先に読み込むかn: 読み込むサイズ